What is BPMN? Business Process Model and Notation
Learn how Business Process Model and Notation (BPMN) helps align teams, empowers more creative problem solving, and speeds up development.
The (not so) secret power of BPMN
Communication isn’t always easy to pull off, especially with modern fusion teams. But a recent study of 755 IT professionals showed that 95% are investing in technologies that have standards-based modeling for collaboration between business and IT users.
Enabling clear and effective communication is especially important for organizations undertaking these initiatives. Because end-to-end business processes are complex, they often span various departments, people, and external systems. The complexity of the process and the diversity of technology running in the background can make it difficult to show exactly what’s happening.
What is BPMN?
Business Process Model and Notation (BPMN 2.0) was developed as a graphical notation to represent complex processes and address these challenges. It is maintained by the non-profit The Object Management Group (OMG) and employed by numerous organizations globally. The visual nature of BPMN enables greater collaboration between different teams, which isn’t surprising given that studies have shown that the human brain can process visuals 15.4 times faster than text.
With an open standard like BPMN, you’re able to:
Get everyone on the same page with process models
Creating visual process models helps everyone better understand, discuss, and remember processes. Because BPMN represents a process graphically, humans of different backgrounds and expertise can read the model.
Visually representing a complex process helps to break down barriers between what’s needed from the business and what’s technically feasible. It allows teams to agree on a chosen design before writing any code. From this foundation, teams can iteratively improve a process using data from the process itself.
Bring visibility to complex processes
Most employees have a limited understanding of the processes and workflows that keep their organization running. Their view typically covers their specific area of expertise, resulting in a fragmented picture of a process that can hinder collaboration and innovation.
BPMN tools should offer various ways to work on and share a process model to better enable cross-team collaboration. With the rise of distributed teams, having ways to design a model remotely (and asynchronously!) can greatly impact productivity and creativity.
Other examples include embedding a model directly on an internal webpage so everyone can understand how workflows run or sharing a process health dashboard. Providing an artifact also ensures that knowledge isn’t lost if the person who created the processes moves to a different team or business unit.
Turn expertise into innovation
Having a diverse set of people working together on the same problem produces more innovative results. Combining technical and non-technical teams to work through a challenge helps uncover gaps in knowledge and create a more holistic and innovative solution.
Developers typically are less interested in the monetary side of the business equation. They’d rather solve complex problems by writing code. But successful collaboration between both parties can be challenging without a simple way to map out and diagram a process.
BPMN can also help teams take a more agile approach to solve problems. You can quickly create a minimum viable product (MVP) solution that addresses the issue you’re trying to fix. From there, you can make data-backed improvements iteratively and deploy the newest version during the next development cycle.
This is where BPMN can help align different groups to better understand and represent a process design. Combining the visual nature of BPMN with a user-friendly way to model processes speeds up the creation of innovative solutions.
Streamline development efforts
Because BPMN can be made executable, a process can be fully designed before any development time is spent. Developers don’t have to waste time writing code that will be revised during a second iteration because everyone aligns on the scope and solution upfront.
Other benefits for developers include:
Less time needed agreeing on the scope of the process solution
Greater focus on implementing the business logic itself instead of routing and orchestration
Enhanced efficiency for process execution
Streamlined development efforts via reusable boilerplate code and Connectors
Out-of-the-box scheduler and durable state using a workflow engine with BPMN
Easier solutions to common engineering problems, such as applying the saga pattern
Reduced coding overhead with advanced symbols like timers, compensation, and gateways
Common workflow patterns BPMN helps solve
Business processes often have similar challenges regardless of the industry or use. As a result, there are several workflow patterns have been created which can solve these problems.
These patterns handle complex business process logic across multiple endpoints, such as executing process flows in parallel, message correlation, escalating events, or dealing with a fatal error.
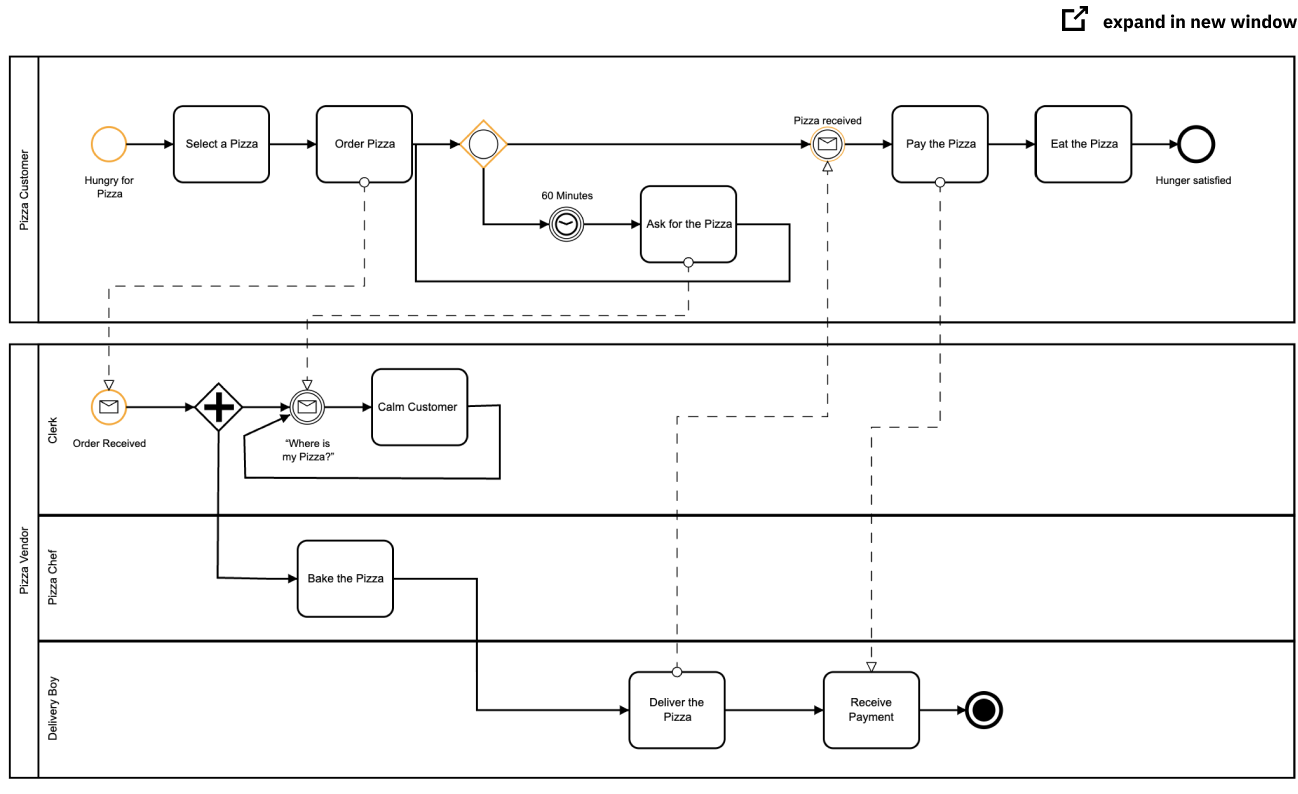
BPMN diagram example
This is a frequently-cited BPMN example developed by OMG to show collaboration between various participants in a process. Because we want to explicitly model the interaction between the customer ordering a pizza, and the vendor who’s producing it, we instead classify them as participants and give each a dedicated pool.
BPMN pizza example
Advanced workflow pattern examples
Dynamic parallel execution
BPMN makes it easy to diagram and coordinate many concurrent tasks.
A simplified example: A customer of an e-commerce vendor purchases multiple items in the online store. During the order process we need to iterate over the list of placed items to make sure they are still available in the vendor’s warehouse.
These steps would also likely inform other systems in the business such as ERPs in finance, customer relationship software, or supply chain and logistics systems.
BPMN simplifies the difficult task of connecting unique identifiers and canceling process instances.
A simplified example: After attempting to cancel an order using their account portal, a customer calls the contact center for help. Unfortunately, the agent lacks details of what the customer already attempted, and doesn’t have a unique ID to reference and help resolve their issue.
Interrupting a workflow with hundreds of tasks spread across multiple distributed systems can be difficult to accomplish at scale without using BPMN and a workflow engine.
BPMN helps escalate a process if it’s not completed within an agreed window of time.
A simplified example: A professional services firm issues an invoice to a customer, and the invoice is not paid on time. An accounting software system prompts the customer to pay the invoice with an automated email coming from the service provider’s business email address.
In this case, the process is coordinated across both the firm’s business email and accounting system.
Three BPMN Myths Debunked
Folks who aren’t familiar with BPMN can sometimes feel overwhelmed by the volume of options. The nature of BPMN is that it can communicate complex workflows in a visual way, but to do so, requires a set of symbols.
Complex
The notation was designed to visually describe complex business processes that span various endpoints such as people, systems, and devices.
To accomplish this, it needs to handle just about any scenario. The result is a “visual language” that helps address process complexity and endpoint diversity through a library of human-readable symbols.
The visual nature makes the notation more accessible because anyone with a little time can pick up the symbols and understand how a process flows.
You can also learn iteratively without needing to recognize every symbol. This lets you start modeling processes with a basic symbol set before revising your models with more advanced complexity.
Difficult To Learn
Any new skill can feel difficult when you’re just starting.
Take your first programming language as an example. There were all these foreign commands, syntax, and specific rules you needed to follow but didn’t yet fully understand.
BPMN is often described as a visual programming language for similar reasons. It has a set of symbols and grammar that you’ll use to describe a complex process.
When learning anything new, it’s a balance of theory and practice that helps you get up to speed fast.
Because it is an open standard, there are plenty of educational BPMN resources available to help.
Obsolete
BPMN has a long history of use to automate business processes.
While some argue that the age of the notation shows that it’s obsolete, the reality is that it is a reliable and effective way to map complex business processes so they’re easier to understand and transform.
A 2022 study showcased how BPMN enhances the efficiency and efficacy of healthcare organizations, and improves patient outcomes while restraining costs.
Because it’s an open standard, BPMN knowledge can easily transfer to other organizations or technology solutions.
Additionally, other standards like DMN (Decision Model and Notation) boost BPMN’s functionality and is still under development. DMN is used to automate decisions helps to fully embrace the potential of your processes.
7 tips to quickly learn BPMN
Adding new skills to your toolkit is a continuous process for developers. There’s always a new technology or language that you can learn to improve your work experience. Because BPMN is an open standard, adding it to your skillset can bring new career opportunities you’d want to explore.
Below are some tips and best practices to learn BPMN and start quickly.
1. It starts (and ends) with an event
There are over 100 unique elements that make up BPMN. For some, that can be overwhelming to start with.
Fortunately, you can begin by looking at just two groups of symbols; flow objects and connecting objects. From there, you can keep expanding your understanding by putting BPMN into practice by modeling processes with greater complexity and more advanced BPMN symbols.
Events
Describes a trigger that either starts, modifies, or completes a process.
Activities
Represents an action (a task) that is taken, whether by technology or humans.
Gateways
These describe a decision point in a workflow, such as parallel (AND), exclusive (XOR), and Inclusive (OR) gateways.
Flows
Connecting objects like associations, sequences, and message flows show how elements relate.
Want to gain a full view of everything related to BPMN?
Download the first 40 pages of the best-selling BPMN book, Real-Life BPMN.
2. Use swimlanes to show responsibilities across processes
BPMN 2.0 defines two different types of swimlanes to partition responsibility for different parts of an end-to-end process: pools and lanes.
Pools act as a container to assign a set of tasks in a process and visually differentiate two or more independent processes. Pools contain lanes, which assign responsibility for subprocesses and tasks to show who is executing the tasks. BPMN calls this type of visualization a collaboration diagram.
Pools should be clearly named with the name of the end-to-end process, for example, Customer Onboarding. You can designate as many lanes as you’d like, but they always exist within a pool.
To get started quickly, you can eliminate pools and only use lanes by modeling the sequence as normal tasks. However, avoiding pools in your diagrams limits your ability to produce diagrams that can represent real-world complexity.
In practice, lanes are often used to assign:
- Positions in the organization, e.g., accounting clerk or logistics manager
- Roles in the secondary organization, e.g. data protection officer
- General roles, e.g. customer or end user
- Departments, e.g. sales
- IT applications, e.g. CRM system or legacy system
3. Watch how experts design complex business processes
Since BPMN has a long history, several experts are producing educational content to share their knowledge. Our Developer Relations team here has produced many videos and other content to help explain the power behind BPMN.
Plus, we have several champions in our community that also produce independent content on the subject. Given BPMN’s proven stability and history, there’s no shortage of experts to learn more.
4. Start with modeling a familiar process
The fastest path to learning something new is pairing theory with hands-on practice. It’s often easiest to start with a process that you’re already familiar with and that’s relatively simple. Another tip is to model a process that you may want to transform through automation to get a tangible benefit from your learning. The key here is to start with a pilot project to keep your education focused and practical.
There are several free BPMN modeling tools are available to you, with some of the most popular ones being created here at Camunda.
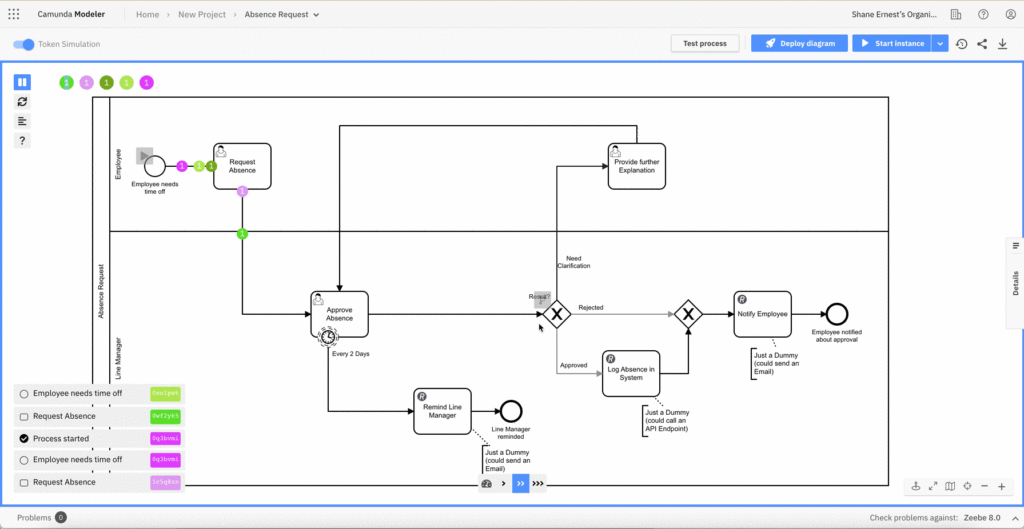
5. Understand process flows with token simulation
Complex models are hard to understand. You can follow the flows by hand, but it’s easier to use token simulation. You can turn gateways on and off to see how they interact with the workflow.
Not every BPMN modeling tool offers token simulation. Fortunately, we have it available in our Web and Desktop Modeler applications.
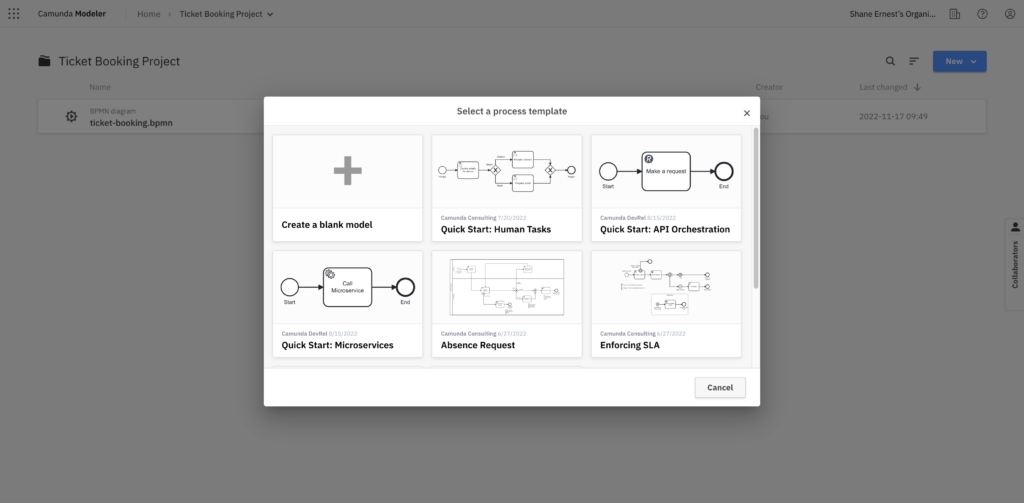
6. Get inspired with pre-designed templates
Every business has uniquely tailored processes. Even the same process, such as a customer onboarding process, will completely differ in implementation and customer experience from one company to the next. This level of customization for common workflow patterns makes BPMN special.
Camunda Web Modeler offers a variety of quickstart templates that can help inspire your process and help you learn BPMN in Camunda. It offers a starting place that you can customize to your specific needs.
7. Learn BPMN online or in person
Because BPMN has a popular global following, there are several ways you can continue growing your expertise. Below are a few of our (semi-biased) favorites you can take advantage of.
Camunda Academy provides anyone with free, unlimited on-demand training on subjects like BPMN, DMN, and Camunda.
Join the Academy
BPMN in Action
The ultimate educational video series for BPMN tutorials. Review best practices, situation patterns, tips and tricks, and more.
Watch videos
CamundaCon 2024
Whether you’re a Camunda newbie, long-standing community member, or process automation pro, you’re welcome to join the event and level up your Camunda knowledge, share experiences and ask questions.
Learn about CamundaCon
“With BPMN, I can show a flow to my business partner, and the business team can easily understand what’s going on. The technical team can understand what the implementation is, and we can model different errors and the process for recovering from these errors.”
Gustavo Arjones, CTO
Itau Unibanco